Android Space
Android Space can be defined as below –
"Space view is a lightweight view subclass that are used to create gaps between different views"
Attributes of Android Space
Some of the popular attributes of space views are –
| S. No. | XML Attributes | Description |
| 1 | android:id | This is unique id of the space to uniquely identify the space. |
| 2 | android:background | Set background of the view. |
| 3 | android:longClickable | Defines whether this view will respond on long click. |
| 4 | android:padding | Set padding of the view. |
| 5 | android:visibility | Set visibility of the view. |
At first, we will create android application. Then, we'll use android space in this application.
Follow the steps below to create new project. Please ignore the steps if you've already created a new application.
| S. No. | Steps |
| 1 | Open Android Studio. |
| 2 | Click on Start a new Android Studio Project Write application name as Space. Then, click next button. |
| 3 | Select minimum SDK you need. However, we have selected 14 as minimum SDK. Then, click next button |
| 4 | Then, select Empty Activity => click next => click finish. |
| 5 | If you have followed above process correctly, you will get a newly created project successfully. However, you can also visit tutorial to Create a New Project to know steps in detail. |
Now, we will modify xml and java file to use space in the application.
Modify Values folder
No values folders have been changed. So, we're not going to mention them here.
Space in xml file
Open res/layout/activity_main.xml file. Then, add below code into it.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Line 1, notice the SPACE below it"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textStyle="bold"/>
<Space
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="20dp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Line 2, notice the SPACE above it"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textStyle="bold"/>
</LinearLayout>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
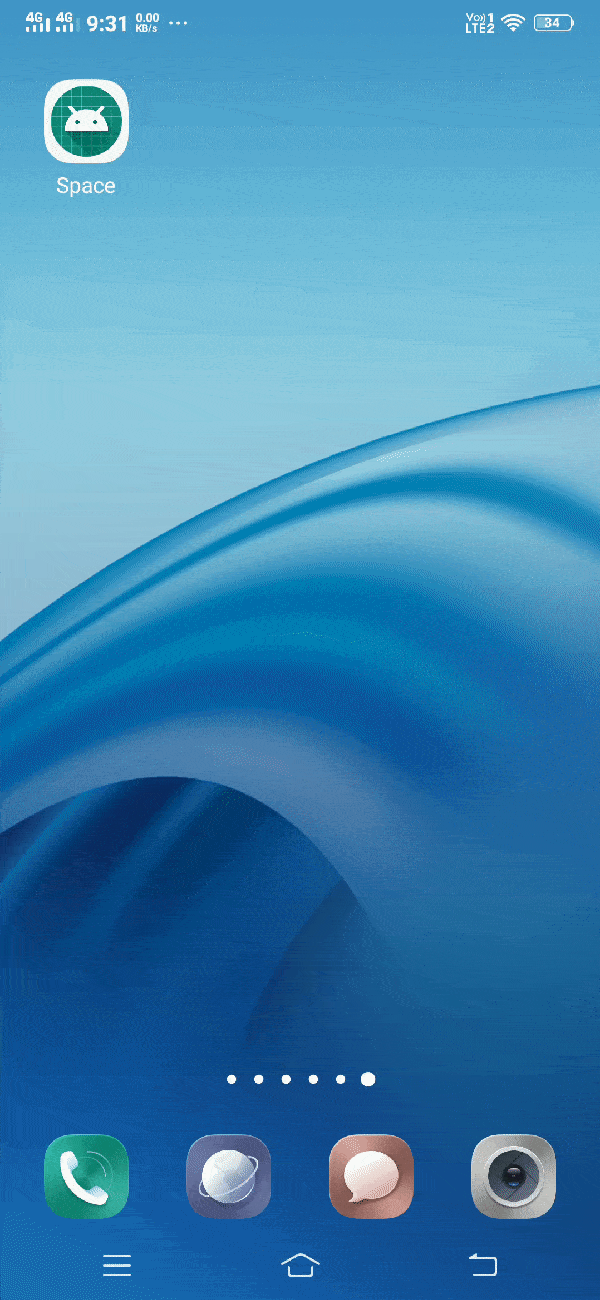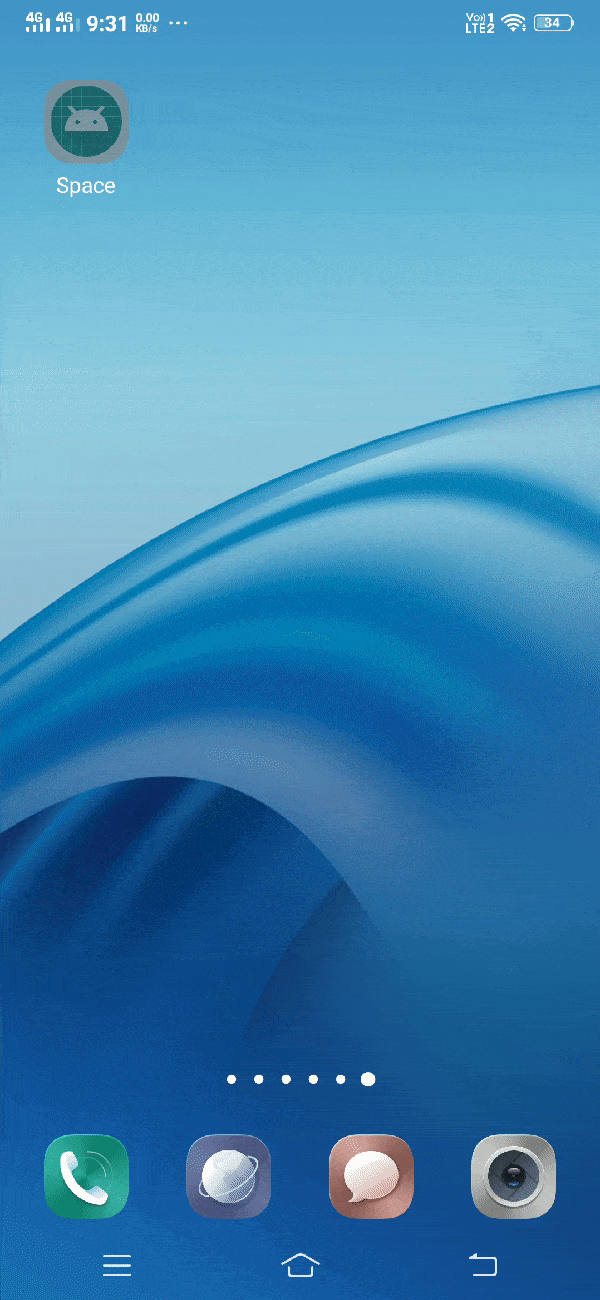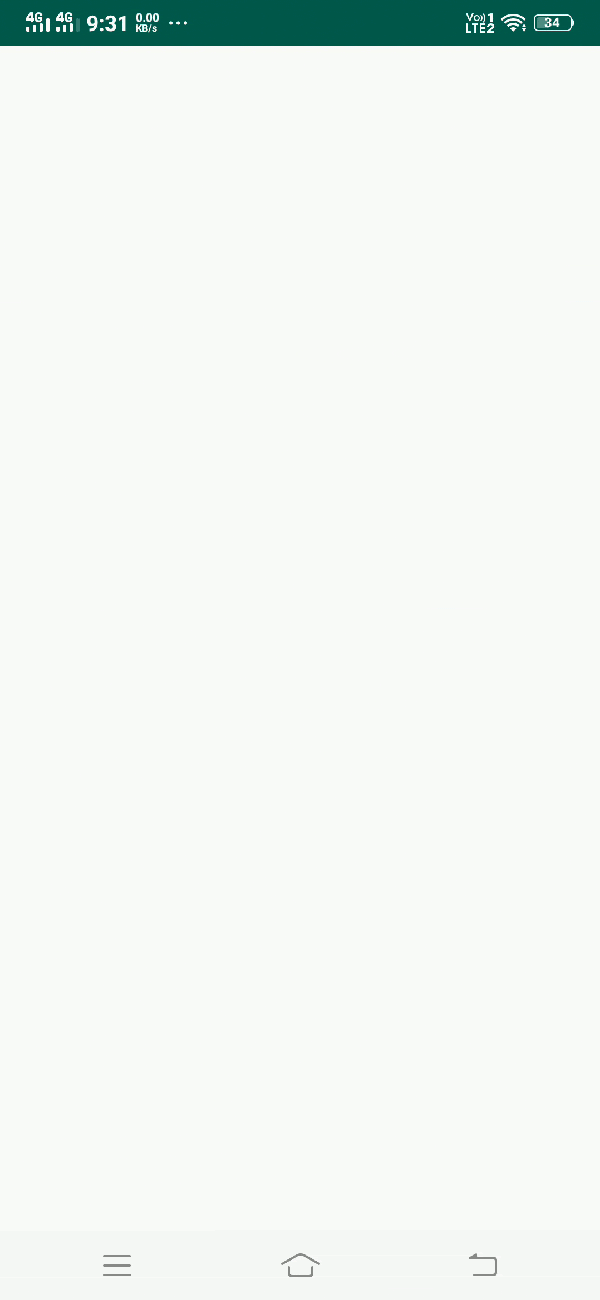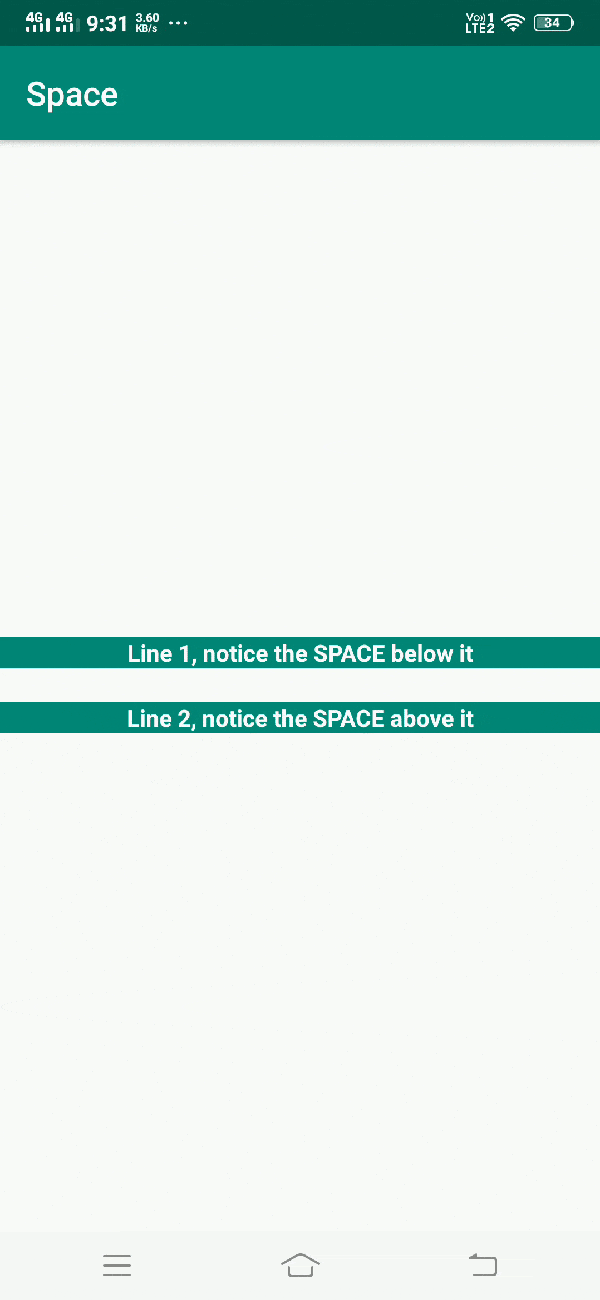
In activity_main.xml file, we have used Space to show space between two textViews. Since androidManifest.xml file is very important in any android application, we are also going to see the content inside this file
AndroidManifest.xml
Code inside src/main/AndroidManifest.xml file is as below –
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.ukacademe.space">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
When you run the application, you will get output as shown below.
Output